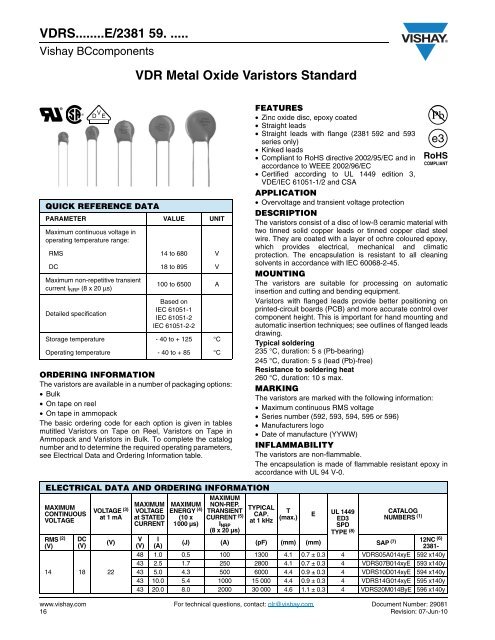
Since a metal oxide is used in its construction the ability to absorb short voltage transients and the energy handling capabilities are extremely high.
Metal oxide varistor function.
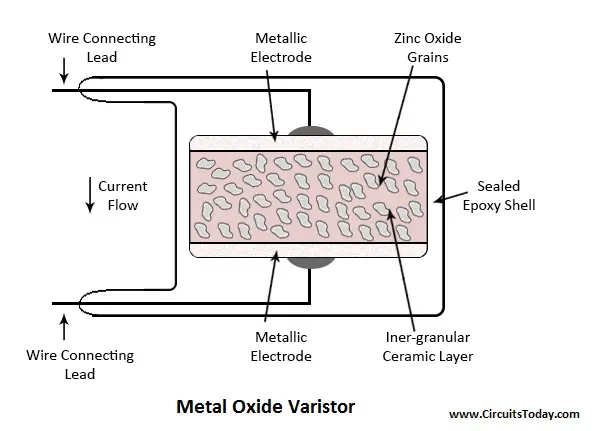
The ceramic powders of the metal oxides are kept intact between two metal plates called the electrodes.
Mov is the most commonly used type of varistor.
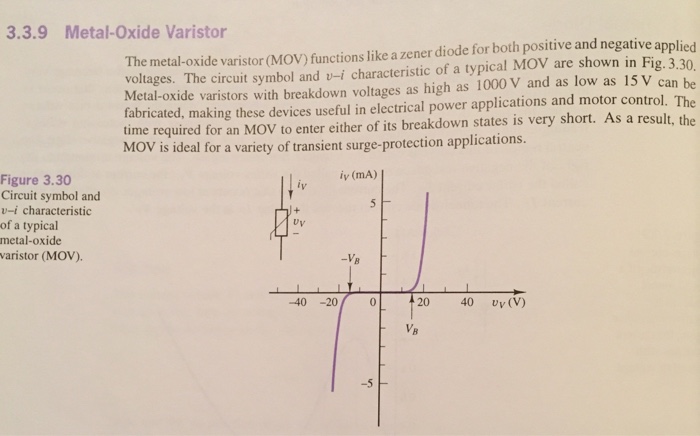
The metal oxide varistor or mov is a voltage dependent nonlinear device that provides excellent transient voltage suppression.
Metal oxide varistors are the most commonly used components that are used as voltage clamping devices to protect small or heavy devices from transient voltage surges.
The metal oxide varistor is designed to protect various types of electronic devices and semiconductor elements from switching and induced lightning surges.
Varistors are used as control or compensation elements in circuits either to provide optimal operating conditions or to protect against excessive transient voltages.
Varistors also called metal oxide varistors movs are used to protect sensitive circuits from a variety of overvoltage conditions.
This type is commonly known as the metal oxide varistor mov.
A mov consist of approximately 90 of zinc oxide and a small amount of other metal oxides.
A metal oxide varistor mov is a protection component used in power supply circuits that is powered directly from ac mains.
Metal oxide varistor is a voltage dependent resistor that is made with ceramic powders of metal oxides like zinc oxide and some of the other metal oxides like oxides of cobalt manganese bismuth etc.
When exposed to high transient voltage the mov clamps voltage to a safe level.
Metal oxide varistors are now the most common type of voltage clamping device and are available for use at a wide range of voltages and currents.
Essentially these voltage dependent nonlinear devices have.
It is used to protect the circuit from high voltage spikes by varying its resistance.
They are reflow and wave solderable and include the ch sm7 sm20 mle mhs ml and mln series.
Metal oxide varistors consist of approximately 90 zinc oxide as a ceramic base material plus other filler materials for the formation of junctions between the zinc oxide grains.